
Further, most relays are non-latching, and will require a steady control current to stay switched. The required coil current varies from tens of milliamps to tens of amps depending on the model, and is achieved with control voltages upwards from 3V. Relays take a substantial control current through their coil to actuate, and may be heavy to switch directly using an Arduino.
As noted, power MOSFETs cannot be used to switch AC current, and do not have corresponding ratings. However, the DC current ratings of relays are typically only a fraction of the AC rating due to arc dynamics.Īdvertisements Power MOSFETs are available with DC current ratings from a few amps all the way up to 600 A – the ratings vary over a wider range than those of common relays. Power relays are commonly rated for AC line currents from 2 to 20 amps, although some large models in buildings and heavy equipment can switch substantially more. Although single power MOSFETs cannot switch AC voltages, some configurations of multiple MOSFETs achieve this too. The voltage ratings of MOSFETs vary from 12V all the way up to 1000V. Power MOSFETs, by contrast, can only switch DC voltages. For switching DC, their voltage ratings are substantially lower, typically under 100V. Most power relay models are rated for at least AC line voltages of 110V or 220.240V. The two power switch types differĪdvertisements Relays can switch both AC and DC voltages. 1 Voltage ratingsīoth relays and MOSFETS are available in a wide range of voltage ratings, extending up to kilovolts. Applications AC switching DC switching, PWM Comparison of mechanical relays and MOSFETs in power switching with microcontrollers. < 100 mOhm 1…50 mOhm Service life 50k…100k operations unlimited Size brick, ½…2” length TO packages Price $1…$3 typ. Property Relay MOSFET DC switching 30 VDC (typ.) 12…600 VDC AC switching 250 VAC N/A Current rating 5…20 A (typ.) 2…200 A (typ.) Control voltage 3.3V, 5V 3.3V, 5V Control current 5…100 mA 0 mA DC, transient Switching time 5…50 ms 0.1 … 5 us Isolation 1.3 kV none ON-Resistance, typ. We will finish by looking at how relays and MOSFETs compare in three common modes power switching: AC, DC, and PWM power switching. The comparison is divided into nine sections, and for those of you in a hurry, summarized in the table below. We will next go through the differences between power relays and MOSFETs in more detail, with an eye on hobbyist microcontroller applications.

Relays are better for AC line power switching tasks and MOSFETs DC. MOSFETs are fast, highly efficient with DC and easy to drive, but they are not isolated and cannot switch AC voltages. In short, mechanical relays are robust, safe, and excellent for AC line power switching, but are slower, bulkier, less efficient with DC and trickier to drive with an Arduino. In this article, I will give a quick comparison of mechanical relays and MOSFETs in power switching with Arduinos.

Both types of components are available with voltage and current ratings in hundreds of volts and amps, and, when properly implemented, can do a wide range of power switching safely and efficiently.īut how do relays and MOSFETs actually compare? Which should you pick for each power switching task, and how do they go along with an Arduino or with other similar microcontrollers?

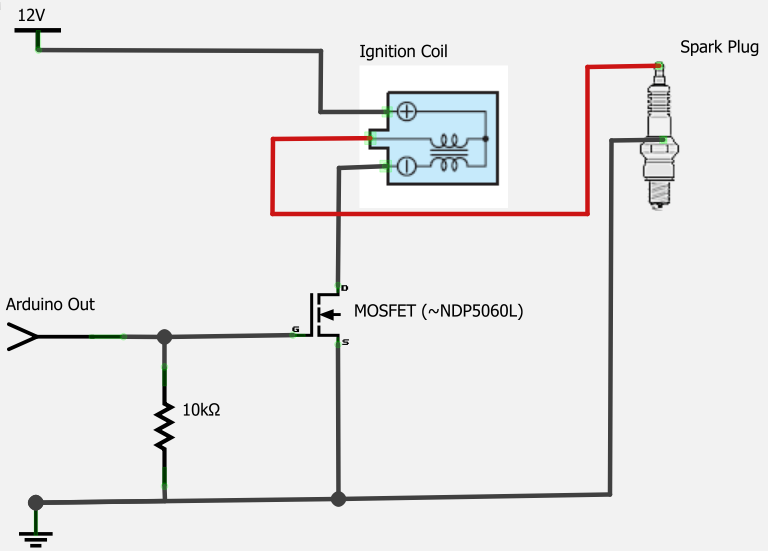
When you want to switch high currents or voltages with an Arduino or similar microcontroller, relays and MOSFETS are likely to be your top component choices for doing the actual switching.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
